Introduction
The website of your business can be viewed as a digital front door for hackers if it is not properly secured. Cyber threats evolve continuously and if you do not monitor them, you risk your site, your users’ data and your reputation. We’ll discuss a comprehensive set of website security tips you can implement now to protect your site, based in part on best practices outlined by expert sources.
What Is Website Security?
Website security is the process of protecting your site from cyber threats like hacking, malware and data leaks. It ensures the safety of sensitive information such as user data, passwords and transactions. Key security measures include SSL certificates, firewalls, regular updates and strong passwords. A secure website builds customer trust, protects your brand reputation and improves SEO rankings. The security of your website safeguards both your business and visitors from online threats, enabling everyone to enjoy a safe and reliable digital experience.
The importance of website security
Before getting into tactics, it’s important to understand the stakes:
- Websites with small audiences are frequently targeted. Roughly 43% of hacked websites belong to small businesses, because attackers look for weak links.
- Data leaks, site downtime and viruses can damage your brand, lead to legal liability and require costly cleanup efforts.
- User trust and SEO suffer when security is compromised browsers may reject insecure sites and search engines favor encrypted, safe sites.
Website security is not a one-time task. It’s a continuous process of monitoring, updating and defending.
Understanding the tactics and attacks of hackers:
How to protect your website from hackers
Understanding how hackers work is crucial to protecting your website. Cybercriminals use tactics like phishing, brute-force attacks, malware injection, SQL injections and cross-site scripting (XSS) to take advantage of weaknesses and gain unauthorized access. They often target outdated software, weak passwords or unsecured file uploads to compromise websites.
Implement strong security measures, such as updating your CMS and plugins regularly, using HTTPS with SSL certificates, setting strong passwords with two-factor authentication, installing firewalls and monitoring your site for suspicious activity. The combination of awareness of hacker strategies and proactive security measures will help you significantly reduce risks and safeguard your website.
12 Essential Website Security Tips You Should Use
Here is a curated, practical checklist to shield your website from cyber threats:
1. Start with a Secure Hosting Provider
Your web host is the foundation of site security. A secure hosting provider ensures that your website is built on a secure infrastructure with strong security measures in place. They offer features such as regular backups, SSL certificates and firewalls to protect your site from potential threats. It is important to choose a reliable host in order to reduce the risk of server attacks and unauthorized access, protecting your information and site.
Choose a host that offers:
- Hardened infrastructure and secure server architecture
- Integrated firewalls, malware scanning, DDoS protection
- Daily backups and disaster recovery plans
The best hosts actively protect your site, not just keep it operating.
2. Install SSL / Use HTTPS Encryption
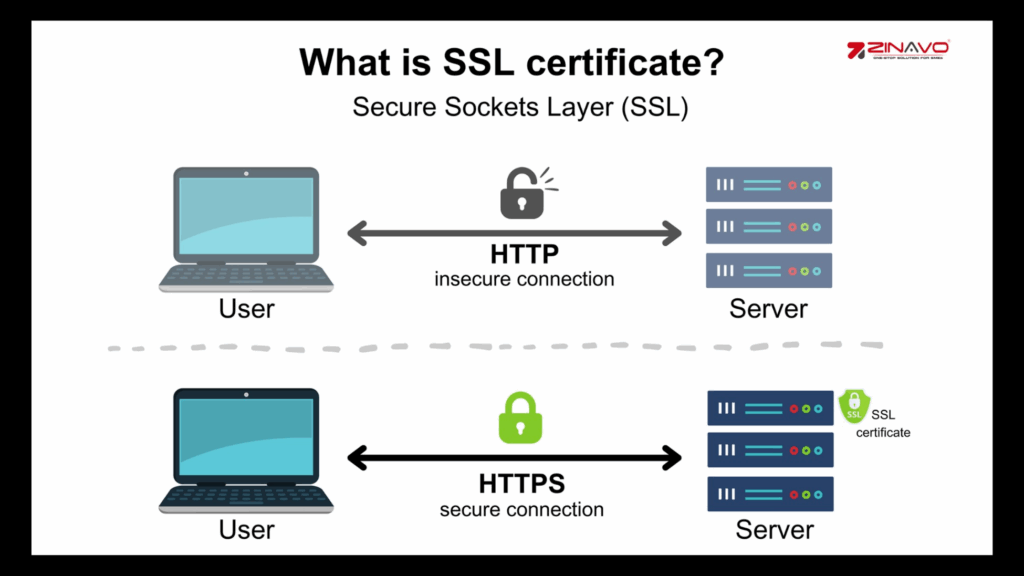
Encrypt data exchanged between your server and visitors by installing a valid SSL certificate. The first step in obtaining an SSL certificate is to choose a trustworthy Certificate Authority (CA). Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) from your server, which includes your domain name, organization details and public key. Once the CSR has been submitted, the CA will confirm the information and will issue your SSL certificate, which can then be installed on the server to secure your website.
This is important for:
- Protecting sensitive information like login credentials or payment forms
- Maintaining user trust and preventing browser warnings
- Boosting SEO, since secure sites are favored by search engines
Many hosts provide free SSL (e.g., Let’s Encrypt) and auto-installation.
3. Use Strong, Unique Passwords & Rotate Periodically
Weak or reused passwords are major security risks. Your passwords may be compromised by an attacker, allowing them to steal sensitive information and even install dangerous software on your computer. Weak passwords are also more susceptible to brute force attacks, where automated scripts try various combinations until they find the correct one. This can lead to unauthorized access and potential data breaches, causing harm to both your website and its users.
- Create long, complex passwords (use passphrases, special characters and numbers).
- Never reuse passwords across systems.
- Change them regularly and immediately after any potential security event.
- Encourage two-factor authentication (2FA) for administrators.
This greatly reduces the risk of brute-force attacks and unauthorized access.
4. Regularly Back Up Your Website
Backups are your safety net. Performing backups frequently is essential to ensure data recovery in case of any unexpected events. Daily backups are recommended to capture the most recent changes and updates to your website. A backup copy in a different location can further protect your data from loss or corruption. When things go wrong, you need a clean snapshot to restore:
- Automate daily or frequent backups of files and databases.
- Store backups off-site or in a separate, secure location.
- Ensure you have a version history so you can revert to a clean state.
A recent, intact backup can save hours, days or even your business reputation after an attack.
5. Monitor Traffic & User Activity
Traffic surges, odd geographical origins and unusual login attempts often indicate a potential attack. Monitoring tools are crucial for quickly identifying and responding to potential security threats. The software lets you see what users are doing in real time and detect changes that could indicate a breach in real time. Your website will be more secure, protected from cyber threats and maintained by monitoring these tools.
- Use analytics and security dashboards to identify spikes.
- Block suspicious IPs or traffic sources.
- Log all admin and user behavior to review later.
Early detection can often nudge you to defuse potential threats.
6. Run Regular Malware & Vulnerability Scans
Security testing, such as penetration testing should be performed by a professional company. The security engineers will test the resistance of your web environment to cyberattacks and advise you on what security improvements are needed to address the existing vulnerabilities and prevent similar issues in the future. Security checks provide for manual or systematic assessments of a system to determine whether the client is capable of preventing hackers from hacking their website. Take action before trouble arises. Use scanning tools to:
- Detect malware, suspicious file changes or malicious code snippets.
- Discover security flaws (outdated plugins, insecure scripts).
- Notify you immediately when new threats are found
Many hosts or security services offer automated scanning solutions.
7. Stop Repeated Login Attacks
Attackers often attempt multiple login combinations until they succeed. Mitigation techniques:
- Limit login attempts per IP (e.g., lock out after 3–5 failures).
- Login forms must contain CAPTCHA or reCAPTCHA.
- Use 2FA so that even if the password is compromised, access stays blocked.
These steps slow down or stop automated attacks significantly.
8. Use a Web Application Firewall (WAF).
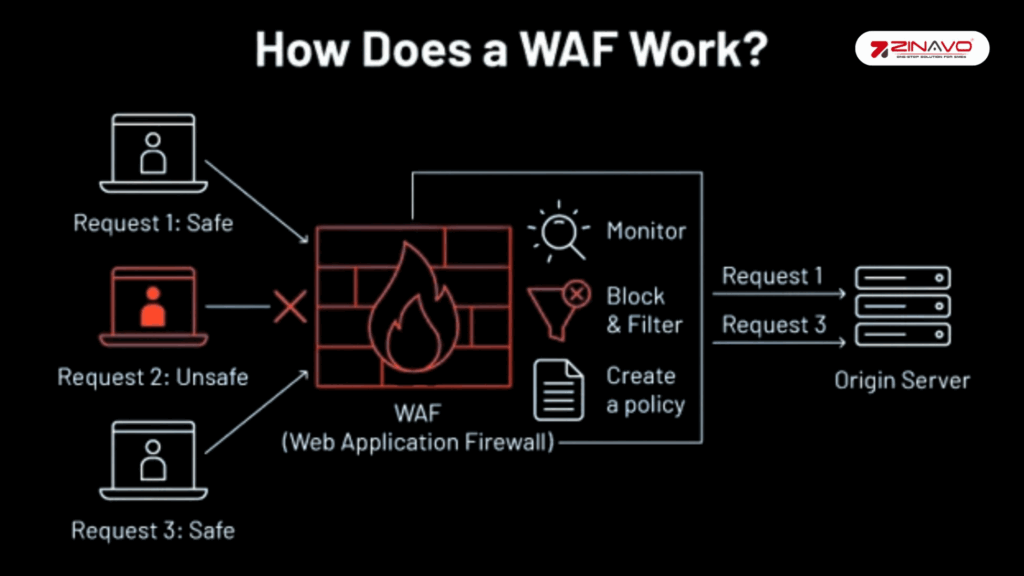
A WAF acts as a security barrier between your website and malicious traffic: Regular updates to your WAF are crucial to ensure it can defend against the latest threats. Cyberattack techniques evolve rapidly and without updates, your WAF might not recognize new risks or attack patterns. Keeping it updated ensures that your web application remains protected from emerging threats and maintains a strong security position.
- Filters out unwanted requests (SQL injection, XSS, bad bots)
- Optionally operates at server level or via plugin
- Some hosts provide managed or built-in WAF, which is generally more robust.
9. Stay Updated on Core System, Themes & Plugins
Regular updates are essential to patch known bugs and improve system security. The more frequently you update your core system, themes and plugins, the less chance an attacker can use outdated software. Consistently updating ensures that you are equipped with the latest security enhancements and features designed to protect your website from potential threats. Many attacks utilize outdated components.
Reduce the risk by:
- Updating your CMS core, themes and plugins immediately when patches are released
- Removing unused or unsupported plugins/themes entirely
- Choosing extensions from reputable, maintained sources
Software updates often contain crucial security patches.
10. Harden Admin & Login Area
Implement measures such as changing the default login URL to make it harder for attackers to find. Additionally, enforce strong password rules, requiring complex passwords that combine letters, numbers and symbols. Consider IP whitelisting, allowing only trusted IP addresses to access the admin area for added security. Make admin access harder to target:
- Rename or move default login URLs (e.g., avoid /wp-admin or /wp-login.php).
- Disallow “admin” or default usernames.
- Enforce login delay or two-stage login.
- Use security plugins or tools to lock down critical directories.
These small changes raise the difficulty for attackers.
11. Manage User Roles & Permissions Carefully
The creation of a user account on your system introduces a potential security risk. It is important to grant no more privileges than are necessary, following the least privilege principle, in order to minimize vulnerabilities. Regularly review and disable unused or inactive accounts to prevent unauthorized access through forgotten credentials. Websites with multiple editors or administrators should also separate content creation from security and administrative rights. This approach ensures that even if one account is compromised, the potential damage remains contained and limited, helping to maintain the overall security and integrity of your website or system.
12. Install a Reputable Security Plugin or Tool
The use of a reliable security plugin on platforms such as WordPress can simplify and automate essential security tasks. Plugins centralize firewall management, malware scanning and login protection, providing multiple layers of defense. The system also monitors file integrity and detects suspicious activities, ensuring that your site is protected from unauthorized changes. The majority of quality plugins also provide detailed activity logs and real-time alerts, allowing you to react quickly to potential issues. When choosing a security plugin, always look for one with strong developer support, frequent updates and a proven reputation to ensure your website remains secure and up to date.
Making Security a Continuous Priority
Implementing these twelve measures is foundational but maintaining security is ongoing. Here are some key practices:
- Regular reviews – audit your security setup quarterly.
- Stay informed – monitor security news, patches and security disclosures.
- Train your team – educate all users on phishing, safe login habits and recognizing potential threats.
- Test your defenses – perform penetration testing or hire security audits.
These steps will help you stay ahead of evolving threats and adapt swiftly.
Conclusion
The ultimate goal of securing your website is to prevent cyber threats on an ongoing basis. The security risks of your website can be largely reduced if you use strong passwords, regular updates, reliable backups and trusted security plugins. Prioritizing user access control, monitoring activity and protecting data are essential steps to maintaining long-term safety and trust. Remember, even small security measures can make a big difference in preventing major attacks. Stay proactive and updated and safeguard your online presence.



